The Wooster Tree Ring Lab collaborated on a publication describing the recent thermal history of the Lidder Valley, Northwest Himalaya. Dr. Santosh Shah, the lead author, is a multitalented paleoclimatologist at the Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences in Locknow, India. He and his colleagues led the study that appeared in Climate Dynamics and is titled: A winter temperature reconstruction for the Lidder Valley, Kashmir, Northwest Himalaya based on tree-rings of Pinus wallichiana. Here is the abstract from the study:
Abstract: A regional, 175 year long, tree-ring width chronology (spanning 1840–2014 C.E.) was developed for Pinus wallichiana A. B. Jacks. (Himalayan Blue pine) from the Lidder Valley, Kashmir, Northwest Himalaya. Simple and seasonal correlation analysis (SEASCORR) with monthly climate records demonstrates a significant direct positive relationship of tree growth with winter temperature. A linear regression model explains 64% of the total variance of the winter temperature and is used to reconstruct December–March temperatures back to 1855 C.E. The most noticeable feature of the reconstruction is a marked warming trend beginning in the late twentieth century and persisting through the present. This reconstruction was compared with instrumental records and other proxy based local and regional temperature reconstructions and generally agrees with the tree-ring records and is consistent with the marked loss of glacial ice over the last few decades. Spectral analysis reveals a periodicity likely associated with the Atlantic Multidecadal Oscillation and El Niño–Southern Oscillation. Spatial cor- relation patterns of sea surface temperatures with the observed and reconstructed winter temperatures are consistent with larger scale warming in the region.
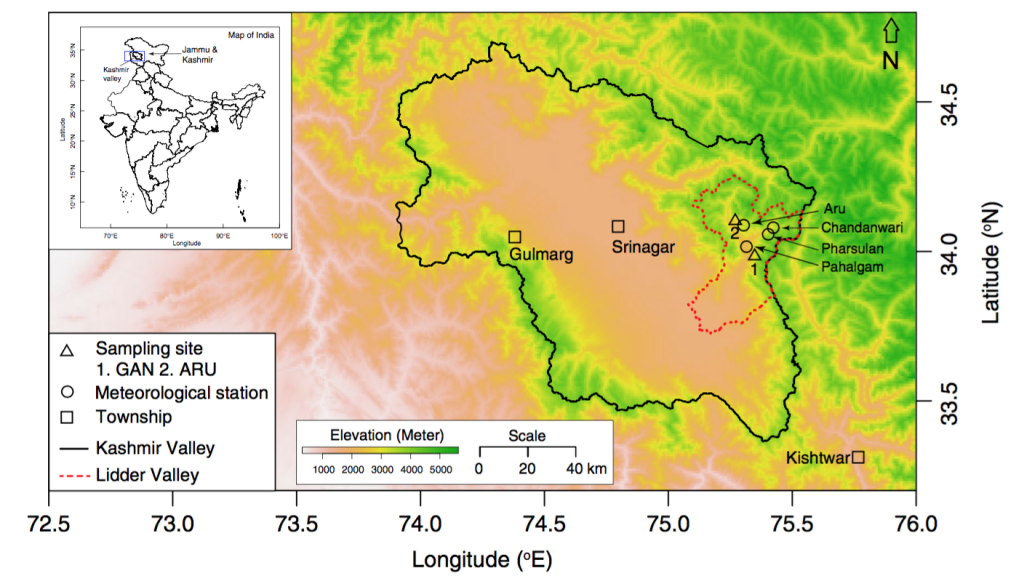
Map showing the location of the study in the Lidder Valley in Kashmir, Northwest India.
The rivers of the Lidder Valley are fed by glaciers from the Himalaya, which are becoming increasingly impacted by climate change and population pressures. The people within the valley depends on the water from the rivers and managing the water in this rapidly warming region is an increasing challenge. The results in this work show the increasing pace of the recent warming (see figure below).
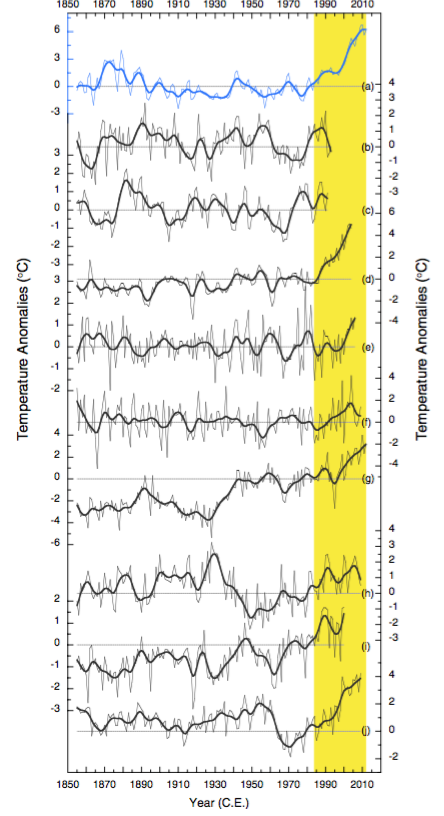
Temperature reconstructions (above) based on tree-rings for the Himalaya. The curve on the top is from the new publication.
Dr. Shah is now working on using tree-rings to reconstruct river flow in the region. This is work that he presented last year at World Dendro in Bhutan and which we are are also collaborators. We are grateful to Dr . Shah for introducing us to climate change research in the Himalaya AND for his help to our former students of the Wooster Tree Ring Lab.
Jeff Gunderson, who recently completed his masters thesis at The Ohio State University in Geography used tree-rings from the Peruvian Andes to reconstruct climate. Jeff collaborated with Dr. Shah who shared his computer code and guidance in calibrating his Peruvian tree-ring records.
Jeff Gunderson, who recently completed his masters thesis at The Ohio State University in Geography used tree-rings from the Peruvian Andes to to tell us about past temperature changes in another region of the world that depends, in large part, on the melting glaciers for water. Jeff collaborated with Dr. Shah who shared his computer code and guidance in calibrating his tree-ring records.
.











